Computer vision in manufacturing is streamlining the use of visual data to make faster and better decisions. Factories become safer, and the production quality increases when manufacturers use insights shared by computer vision systems. We’ll discuss the use of CV in the manufacturing industry in detail.
The manufacturing industry is adopting the latest technology to modernize processes and increase production. Artificial intelligence, cloud computing, machine learning, the Internet of Things (IoT), Industry 4.0, and computer vision are now a part of the manufacturing industry.
Computer vision is used at every stage of manufacturing, right from procuring raw materials to supplying and distributing the finished goods. It has a vital role in bringing flexibility and scalability to the manufacturing unit. It helps increase production while sustaining quality and minimizing the use of resources. Manufacturers hire AI developers and offshore solution providers to digitally transform their infrastructure and integrate it with the latest technology.
Computer vision is a field of artificial intelligence and computer science that empowers devices to read, understand, and analyze visual data as humans do. While AI makes machines think, computer vision makes machines see and understand visual information at the pixel level. Images, videos, and all forms of visual inputs can be read and processed through computer vision.
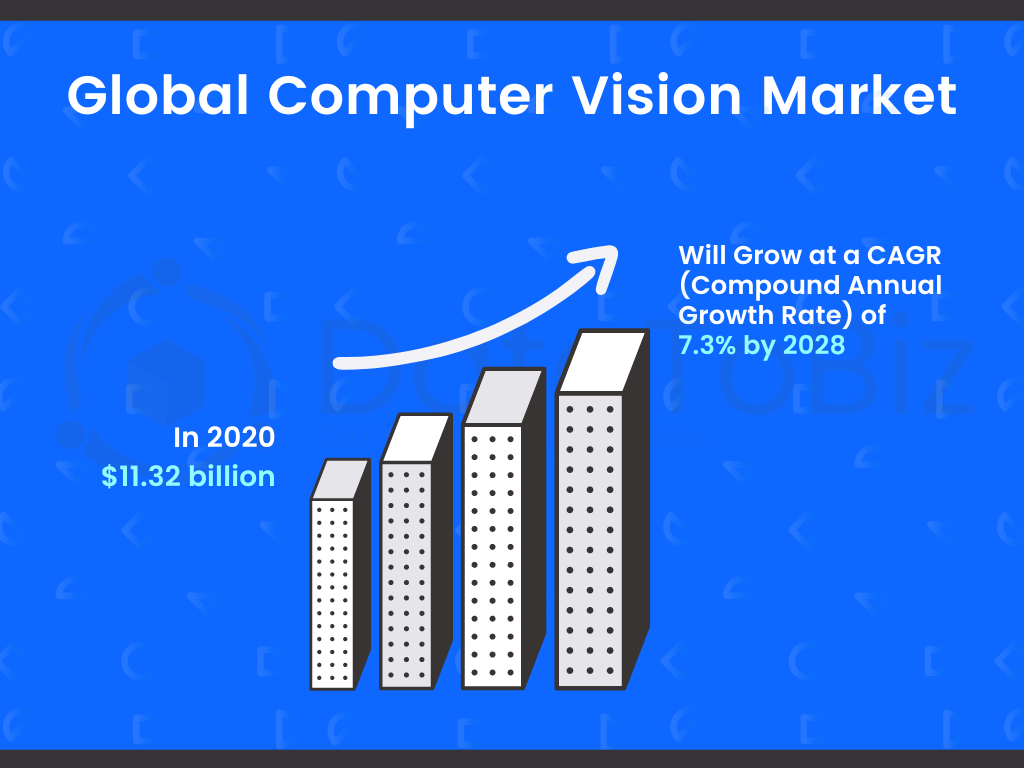
The global computer vision market in 2020 was $11.32 billion and is expected to grow at a CAGR (Compound Annual Growth Rate) of 7.3% by 2028. The industrial segment was responsible for around 51% of the market revenue. Computer vision in a range of manufacturing processes contributed more than half the total global share. The Asia Pacific region had a high adoption rate and contributed 40% of the revenue in the same year.
But how is computer vision used in the manufacturing industry? With more and more manufacturers planning to adopt computer vision and Industry 4.0, how do they intend to change their systems and processes? Let’s take a look.
Computer vision doesn’t require any physical contact with the machinery. It works simultaneously to process the input data from multiple sources and provide insights to the workers, supervisors, and managers.

Computer vision is used to automate the product assembly process. Computer-aided software is used to create 3D designs fed into the system to assemble and manufacture the products. The need for human intervention is minimized by allowing computer vision to assist the machinery in manufacturing the products with greater precision.
Computer vision systems work continuously to monitor the assembly line so that defects are identified in the initial stages. This reduces the returns or rejected products and increases customer satisfaction. Every stage of the assembly process is monitored and tracked. The data is stored in the data warehouse or data lake.
For example, Telsa manufacturing has automated almost 70% of the manufacturing processes using computer vision. The pharma industry uses computer vision to ensure that the quality of the product is consistent and adheres to industry-wide standards.
Predictive maintenance can save millions of dollars for the manufacturing industry. Machinery is the heart of a manufacturing unit. Even a minor breakdown can disrupt the entire process and cause a series of delays that lead to additional expenses. The supply chain will be disturbed when there’s an unexpected halt in production.
Computer vision minimizes such disruptions and losses by constantly assessing the health and working condition of the machinery. Heavy machinery runs for long hours in unusual temperatures and environments. They are prone to breakdowns without proper maintenance and care.
However, instead of being reactive and repairing the machinery after it breaks down, computer vision uses its algorithm to determine the best time to perform a maintenance check and repair the minor issues. This prevents the trouble from blowing up and causing a full-scale disruption. Furthermore, minor repairs take less time and money than major spare part replacements.
Defects are a bane of the manufacturing industry. The product assembly can’t manufacture with complete accuracy. However, the extent and percentage of defects can be a game-changer for the manufacturer.
A computer vision algorithm is trained to identify defects at the micro and macro level. Instead of waiting until the quality testing/ inspection, the products are checked for defects right during the manufacturing process. Even the slightest difference is highlighted so that workers can remove the defective product. Corrective measures can be taken by easily identifying the cause of the defect.
Data from the cameras and processed by the computer vision systems and compared with the database to test for quality and defects. This minimizes the loss of money and reputation by preventing defective products from reaching the end-user.
Molds and dies are an inherent part of the manufacturing industry. Manufacturers spend large amounts of money creating dies to give the products the desired shape and structure. Laser and rotary are two famous methods used to create dies. While high-speed laser light provides precise dies, it cannot cut through tough materials. The rotary technique uses steel blades and physical tools to cut through hard material, but it can be less precise and time-consuming. Computer vision can fine-tune the rotary die-cutting method to make it as precise and fast as the laser technique. In short, computer vision gives the best of rotary and laser methods to increase accuracy and precision in the dies. Since these dies are used to manufacture spare parts and products, the end result will be of better quality. Offshore Artificial Intelligence software development companies can help manufacturers use a computer vision system to guide the die-cutting machine in the right manner.
Packaging is the final stage after manufacturing the product. The package should be strong and capable enough to protect the finished good from damage caused during the shipping and distribution. The package should also ensure that the product inside doesn’t get affected by the changes in the surrounding environment.
Industries like pharma, food and beverage, cosmetics, etc., pay extra attention to packaging. Computer vision systems can analyze the packaging material and highlight the products with weak or bad packaging. The outer package can be changed and replaced before the finished goods are sent to the inventory.
The material, color, quality, type, thickness, etc., of the package, should be consistent throughout the batch. Computer vision can analyze the images and videos of the packages and provide the necessary insights to manufacturers before the goods leave the factory or warehouse.
Computer vision is not limited to monitoring machines and products. It is also used to increase workplace safety and prevent accidents. One of the main concerns in a manufacturing unit is the lack of safety for workers. Accidents happen even when the manufacturer takes all possible safety measures. Loss of life and serious injuries have a long-term impact on the business, management, workers, and their families.
Computer vision uses data from the CCTV cameras installed in the factory to monitor and track the movements of workers around the machines. It is much more efficient than hiring an employee to watch the screens with CCTV camera recordings and alert the workers. Computer vision systems are automated to continuously process visual data and send alerts to the supervisor/ management.
If the accident has already occurred, computer vision will help identify the exact location, cause, and intensity. For example, if there’s a leakage of poisonous gas in a factory, computer vision systems can pinpoint the location where the leakage has occurred. This information helps the workers find another way to escape the factory without walking into the danger zone or risking their lives.
Barcodes contain the product’s information in a compressed format. Every final product has a barcode to identify its batch/ lot, manufacturing details, packaging information, etc. Barcodes are read using a different tool/ app that can process the compressed information hidden in those lines.
So how does computer vision help by reading barcodes on the products? Computer vision accurately reads the barcodes and the printed text to compare with the manufacturer’s database. It confirms that there is no barcode mismatch or gaps in the information provided on the package.
For example, a wrong barcode will lead to incorrect identification of a product and cause confusion among the distributors, retailers, and end-users. Identifying such errors before the stock leaves the premises can prevent confusion and save the time required to correct the barcode.
Managing the stock in an inventory is no small feat. Large enterprises can use computer vision for inventory management and automate stock counting, database updating, sending alerts to managers, and so on. The errors caused by manual stock-taking can be eliminated using the computer vision system.
Machine learning developers can customize an algorithm to help manufacturers, especially warehouse employees streamline inventory management. Computer vision uses data from multiple systems and seamlessly finds the batch/ product the employee is searching for. From arranging the stock to creating more space to alerting the managers in case of low material (for production), computer vision helps with the procurement of raw materials and storing the finished products in the warehouse.
The label is as important as the barcode for a finished product that’s ready to be shipped. A wrong label can lead to loss of life, especially in the case of food, drugs, and cosmetics. Using the wrong medicine or a product with allergic components leads to severe health conditions. This affects the consumer and the manufacturer. Lawsuits, monetary compensation, and loss of reputation are the after-effects of such incidents.
The computer vision system reads the text on the label and ensures that it matches the data in the database. It can also read handwritten notes and signs made by employees when transporting the stock from the factory to the warehouse or warehouse to the end-user. Computer vision can provide complete information about a product by processing its image/ video.
Scrap is the waste by-product of production. Excess scrap indicates an increase in the cost of manufacturing but without a proportional increase in the final products. Every manufacturer aims to reduce scrap and use/ sell it effectively to make up for the difference in the amount.
Computer vision and artificial intelligence algorithms can monitor the quantity of scarp generated at every stage. It helps identify machinery with more scarp generation. Such machines can either be upgraded or replaced with newer models to reduce scrap. Cutting down scrap is a good indicator of optimizing the resources and reducing investment that too without compromising the quality of production.
Industry 4.0 is nothing but the transformation we see in the current scenario. The shift from the traditional approach to an intelligent one by relying on artificial intelligence, computer vision, cloud computing, and edge technology is termed the fourth industrial revolution. AI-based robots are a part of this transformation and help in sharing data, automating workload, and minimizing the pressure on human workers.
Computer vision guides robots in performing complex actions with greater precision. Robots aren’t yet fully capable of taking over manufacturing and replacing human workers. Humans use robots and AI technology to complete their job faster, better, and without risking their lives.
Computer vision can process huge data sets in less time. Once the algorithm is trained, it learns how to see patterns, identify defects, and point out issues. It also learns from the feedback loop to fine-tune the algorithm and minimize errors.
Computer vision in manufacturing is making enterprises energy-efficient and consistent. Improve the quality of production and eliminate bottlenecks by implementing computer vision technology in the manufacturing units. Connect all devices and people to get real-time insights and make the right decisions for the business.
